Display Advertising is the modern-day roadside billboard. However, compared to roadside advertising, display advertising offers significant advantages: it can be targeted based on people's interests or behavior, it is cost-effective, and it can be measured with great precision. Display advertising is an excellent way to create awareness, re-engage, and convert.
In this article, let's explore effective advertising on Google's display network.
What is display advertising?
In roadside advertising, giant billboard structures are used to convey the message. In display advertising, instead of billboards, banners or image ads are used, which are displayed on websites that allow advertising.
Google's display network consists of a total of millions of different websites, and this entire network is available to display advertisers. Below is an example of the basic data for one of our campaigns in a month:
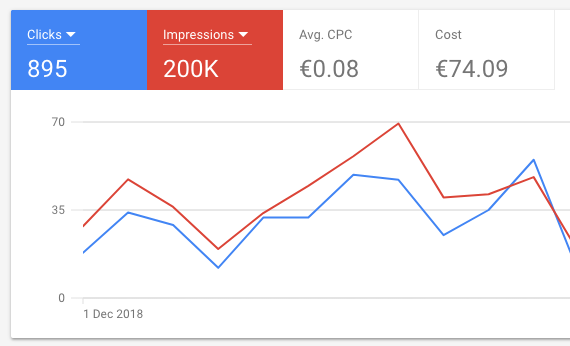
With a budget of 74 euros, the ad has been displayed a total of 200,000 times and clicked 895 times. Quite impressive numbers, wouldn't you agree?
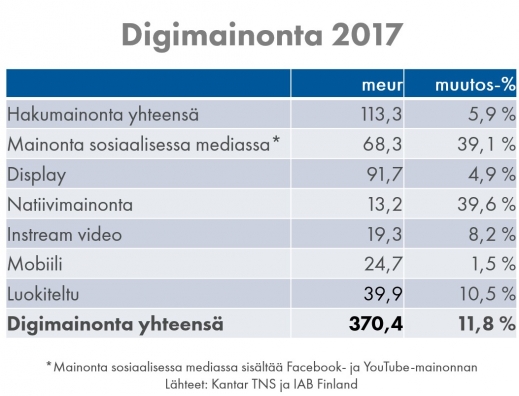
Advertisers also clearly find display advertising profitable, as according to a report by Kantar TNS and IAB Finland, display advertising was the second most popular digital advertising method in terms of euros in 2017.
Who can the advertising be targeted to?
Display advertising can be targeted to both warm and cold audiences.
A warm audience has visited your company's website, so your brand is somewhat familiar to them. The goal of the advertising campaign in this case is either re-engagement or conversion.
A cold audience, on the other hand, is an audience to whom your company's brand is not yet familiar. The purpose of the advertising is to communicate the existence of your company, in other words, to create awareness.
Warm audiences are reached through remarketing.
People pay more attention to ads if they have a connection to the brand shown in the ad. According to eMarketer's research, 58% of people pay attention to ads that feature products they have previously viewed online:
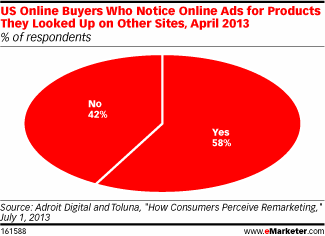
This information should definitely be used to your advantage. In display advertising, this means targeting ads to audiences who have visited your company's website.
The audience that has visited the website can be reached through remarketing. The process works like this: first, a separate list is created for the audience that has visited the website. In this case, a list refers to bundling the cookie data collected by Google into one file, which can then be used as a target audience when creating an ad campaign.
To create the list, the source code of the company's website must have a tag or piece of code that enables remarketing. This can be obtained through either Google Ads or Google Analytics. This tag works by installing a cookie on the user's device when they arrive on your website. With this cookie, Google identifies these visitors and knows how to target them with tailored advertising.
After creating the list, image ads are created and the campaign is launched.
In remarketing, it's important not to target the advertising for too long. I myself visited a software vendor's website six months ago, and they still target me with their ads on YouTube almost daily. The bombardment has been so massive (I've seen the ad an estimated 200-300 times) that I've formed a negative association with that brand in my mind.
Remarketing should be targeted within 14-30 days of visitors' last visit to the website. Below is an image from one of our campaigns, where the audience consists of visitors to the website who have viewed at least 2 pages. The list is open for 14 days, after which ad display is stopped.
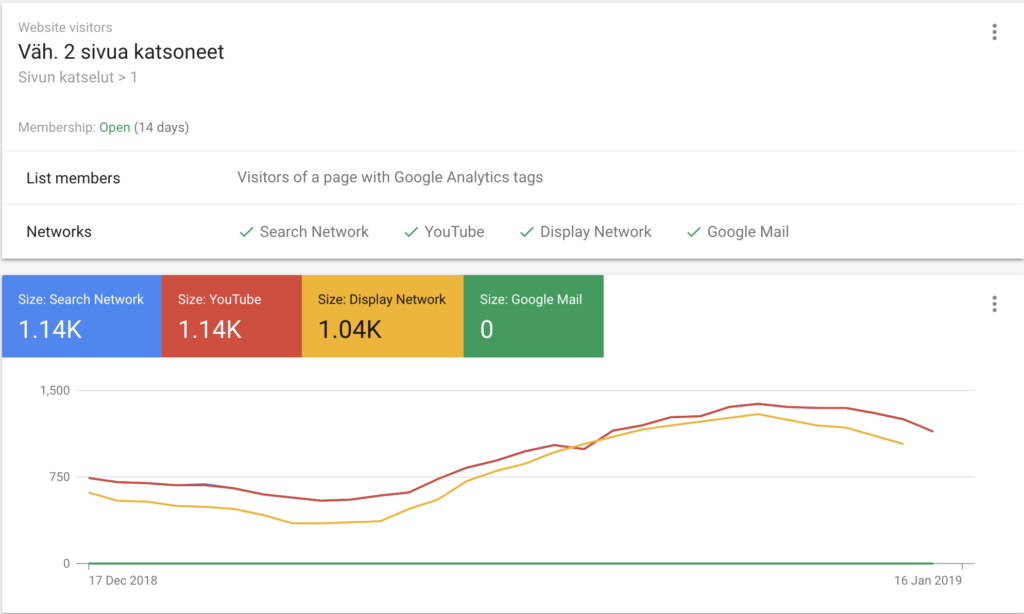
Display advertising can thus target very specific audiences.
For example, an online retailer could target display advertising only to those who have added products to their shopping cart or visited the checkout page. Those who have added items to their shopping cart have clearly expressed an interest in completing a purchase, but the transaction may have been interrupted for some human reason. Cart abandonment, or interrupting the transaction, is common in online retail: on average, only 30% of those who add items to their shopping cart complete the transaction.
When creating audience lists, it's important to consider the size requirements set by Google: for example, in remarketing, the list must have at least 100 active visitors in the last 30 days. In other words, 100 visitors should have abandoned their shopping cart in the last 30 days in order for advertising to be targeted to such a specific audience. The online store must have enough traffic for this condition to be met.
Targeting Cold Audiences
Advertising can also be targeted to cold audiences, meaning an audience that has not visited your website and may have never even heard of your brand.
Google offers a wide range of options for targeting, but the methods can practically be divided into two categories:
Targeting based on Visitor Characteristics (e.g. age and gender) and Behavior
Targeting based on Site Content
When using the classification based on visitor characteristics and behavior, the advertiser does not individually select the pages where the ads appear. For example, an ad for a flower shop might appear on a discussion forum focused on rock music if Google determines that the person is interested in flowers.
Options for targeting based on visitor behavior are as follows:
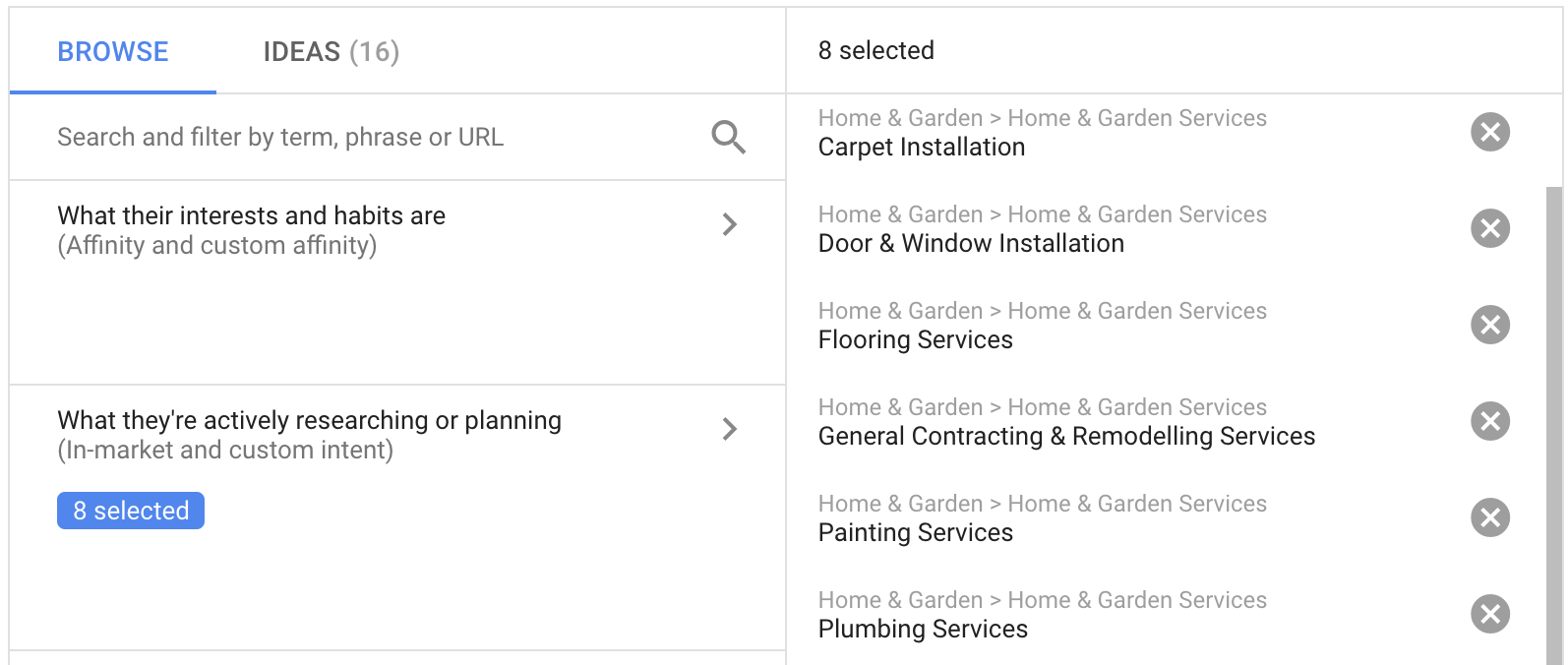
The upper option (affinity) refers to a longer-term interest in a specific topic. These visitors actively visit websites in the field and have shown continuous interest in the subject. From the list, desired interests can be selected according to different categories.
The lower option (In-market & custom intent) allows advertising to be targeted to an audience actively searching for specific topics at that moment. In the In-market option, topics are selected from a dropdown menu based on categories. In the Custom intent option, the audience is created manually based on desired keywords.
Options for targeting based on site content are as follows:
Managed Placements: Select specific websites (exact URL addresses) where you want the ads to appear.
Topic Targeting: Choose topics related to which you want the ads to appear on websites, after which Google finds the sites on behalf of the advertiser.
Keyword Targeting Placements: Select keywords based on which Google finds sites that contain those keywords.
When using site content-based targeting, Google displays ads to everyone who has visited those specific websites. This means that even visitors who may not be particularly interested in products related to that industry according to Google will see the ads.
What Makes a Good Display Ad?
The anatomy of a good display ad is as follows:
Clarity
Since the size of the ads is limited to specific pixels, it's important for the ad to be clear. Don't try to cram too much into the ad; instead, focus on one main point you want to convey in the ad. This could be your company's slogan if you're creating awareness for a cold audience, or an offer related to a specific product if you're aiming to convert visitors who have been on your website.
Visual Appeal
It's important for the ad to present your company's brand in a positive light. Use an image related to your company and brand-specific colors. The advertising should be consistent so that a visitor who has seen the ad can subconsciously connect it to your brand. Google requires the company name to be visible in the ads, so the logo is a mandatory part of the ad, although it's highly recommended to include it even if it weren't mandatory.
Someone seeking inspiration can visit the example ads featured in Bannersnack's blog. For instance, Adobe uses the following types of ads:
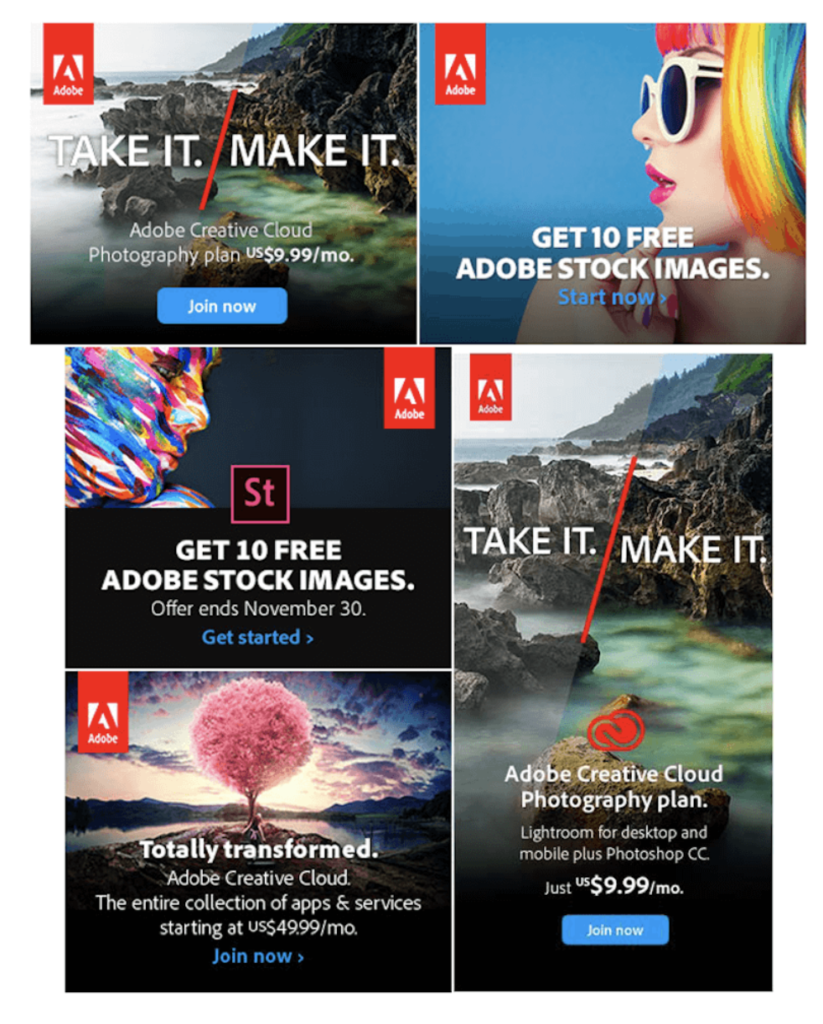
Call-to-Action (CTA)
The call-to-action is usually presented as a clickable button, but it can also be presented as plain text. The buttons and links used in ads are just visual enhancements, as you can click anywhere on the banner and the browser will still direct the visitor to your company's website. It's a good idea to use clear text on the button. In Adobe's ads above, they use "Join now," "Get started," and "Start now" as call-to-actions. They use both buttons and text links as calls-to-action.
Landing Page
The landing page is the webpage that the visitor is directed to after clicking on the ad. The landing page should be as relevant as possible to the ad text. If you're featuring a specific product in the ad text, don't direct the visitor to the homepage of the online store, but rather to the product page for that specific item.
Tips for Creating a Campaign
One of the fundamental rules in Google advertising is to keep display and search campaigns separate. Always.
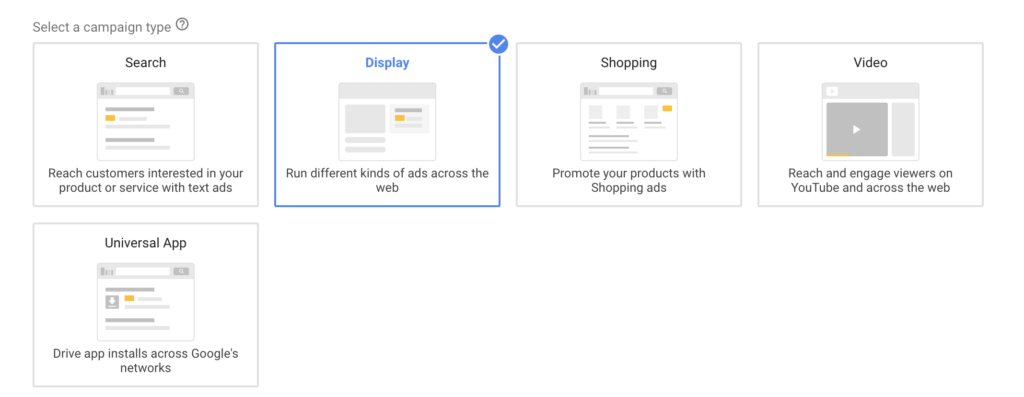
So, when creating a display advertising campaign, select "display" as the campaign type.
When creating the campaign, adjust settings such as:
Geographic locations where ads will be shown.
Language preferences (which language speakers will see the ads).
Bids (the amount you're willing to pay for clicks).
Campaign budget.
Audience to which the advertising campaign is targeted.
Upload the image ads used in the campaign.
It's a good idea to create at least two different ads right from the start and target these ads to the same target audience. This way, you can determine which ad works best based on clean data. The image below is from a normal A/B test of image ads that I conducted in my most recent campaign:
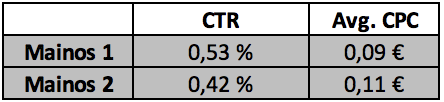
The click-through rate (CTR) of the first ad is 26% higher and the average click cost is 18% lower!
The losing ad can be removed, and a new variation of the winning ad can be created. This way, you can constantly work on improving the effectiveness of the ad.
Before launching the ad campaign, it's advisable to enable conversion tracking! Conversion tracking means tracking the achievement of goals set by the company. In an online store, a conversion is a purchase transaction, and on a website, it could be, for example, filling out a contact form. With conversion tracking, you don't have to guess the effectiveness of the campaign; you can directly see from the data which channel the converted visitors came from.
Summary
Display advertising is an excellent way to promote a company through visual image ads. Advertising can start with retargeting, and the target audience can be expanded using Google's versatile targeting options. The goals of display advertising depend on the target audience: warm audiences are aimed at conversion or reactivation, while for cold audiences, the aim is to create awareness.



